2025/10/15-10/17 We presented our results at the Construction Robot Symposium and received the Outstanding Poster Award.
Smart Infrastructure Management System
Smart Infrastructure Management System
SubprojectA
Innovation in
Construction
Production
Processes
Research Topic Research Topics
What's New What’s New
-
10/15/2025
We presented our results at the Construction Robot Symposium and received the Outstanding Poster Award. -
9/19/2025
Taisei Corporation’s demonstration experiment at Shimokubo Dam was featured in the media -
9/9/2025
Fixed-Point Sediment Monitoring System (3LSB) Installed at Hydropower Facilities

Project Overview Project Overview
What is SIP "Smart Infrastructure Management System"?
The Strategic Innovation Program (SIP) is a national project aimed at achieving scientific and technological innovation through cross-ministry and interdisciplinary management. In 2023, the third phase of SIP includes 14 ongoing projects, focusing on the entire spectrum of research and development, from basic research to practical application and commercialization. More details can be found here (https://www8.cao.go.jp/cstp/gaiyo/sip/index.html)
In our country, a vast number of infrastructure and buildings are aging. To address this issue, one of the projects in the third phase of SIP, "Development of a Smart Infrastructure Management System"(https://www.pwri.go.jp/jpn/research/sip/index.html)」, focuses on the research and development of technologies for integrated infrastructure management. This project leverages digital technologies for the entire lifecycle of infrastructure, from design and construction to inspection and repair. This project aims to establish a system that promotes the development of sustainable, attractive, and resilient national, urban, and regional environments, thereby achieving efficient infrastructure management. Among the sub-projects, we introduce ours, "Innovative Construction Production Process," on this site. This webpage provides an overview of this sub-project.
- Background on the ICAS-Project
-
In the construction industry, policies such as i-Construction by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT) are being promoted to address labor shortages caused by an aging and declining population. In response to this challenge, research and development on the automation of construction sites using Information and Robotics Technology (IRT) is being conducted, primarily by major general contractors. However, previous research and development have been carried out in a closed environment, with major general contractors and related companies forming exclusive groups. This has hindered the entry of new companies and the promotion of innovation.
On the other hand, there are still challenges to be overcome in improving productivity and ensuring safety in areas that are hazardous to humans. For example, dam dredging and the monitoring of volcanic eruptions are highly necessary, but remote and automated operations have not yet been realized. In tunnel construction as well, tasks such as loading detonators and explosives, as well as connecting wires, are still performed by human operators.
The SIP ICAS Project was launched to address the aforementioned issues. ICAS stands for Innovative Construction And Surveillance technology with unmanned machinery.
- Project Objective
-
The aim of this project is to address the aforementioned challenges by minimizing manpower and labor at construction sites, reducing industrial accidents through unmanned measurement and construction, and expediting research and development of remote and automated technologies. To achieve these objectives, we will undertake research and development on the following three themes
R&D theme
-
a-1
Autonomous Earthwork for Total Optimization of Construction Process
-
a-2
Autonomous measurement and construction technology for inaccessible locations
-
a-3
Automated Construction for Tunnel Blasting
-
a-1
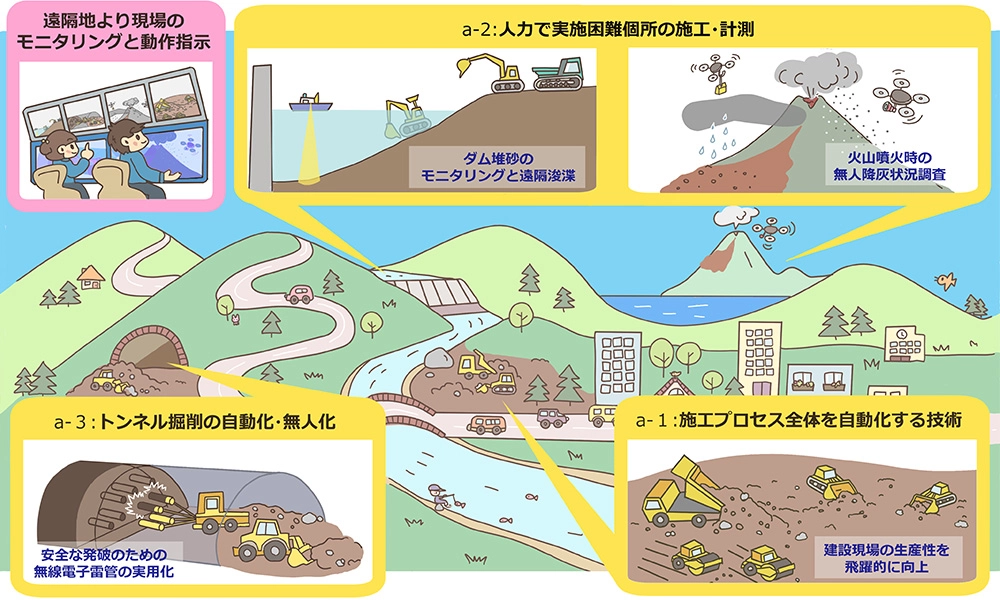
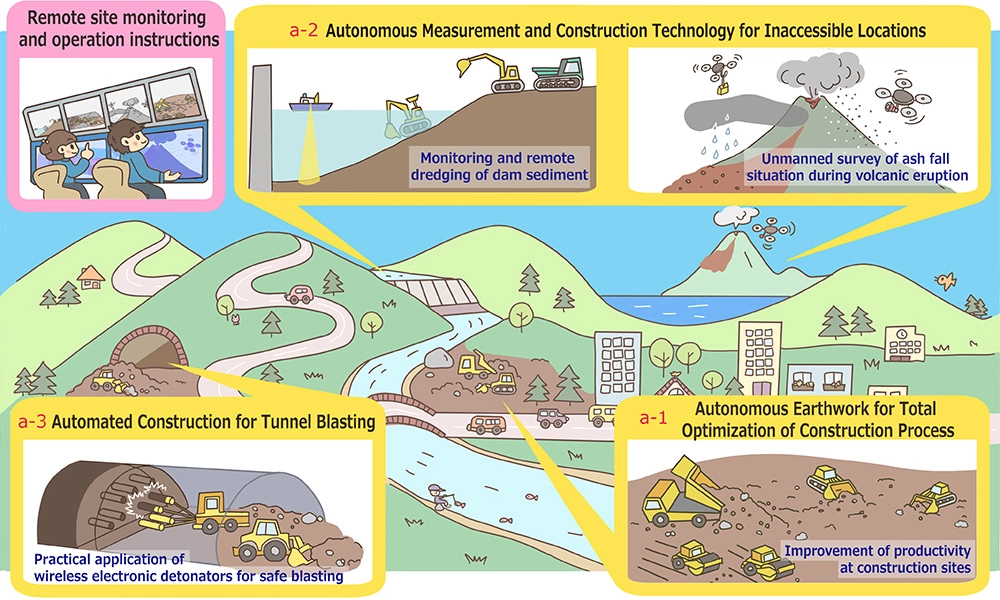
Overview of R&D theme Overview of R&D theme
R&D theme (a-1)
Autonomous Earthwork for Total Optimization of Construction Process
The objective of R&D theme (a-1) is to standardize the information sharing interface between subsystems, such as the planning system and motion management system of construction machines, to achieve automated construction.
Furthermore, based on the system, we aim to realize automated earthworks from construction planning to conducting construction by multiple construction machines. Specifically, the following research topics will be addressed
- Research and development of a construction planning and management system based on an information sharing interface.
- Proposal and evaluation of construction planning suitable for automated construction machinery.
- Cyber-Physical System for RT (Robot Technology) to manage the operation of multiple autonomous construction machines.
- Open R&D environment for automated construction machines.
- Trial in an automated construction site with multiple construction machines.
Each of these R&D activities will be conducted in parallel, and the developed subsystems will be integrated by the end of the third fiscal year. The integrated automatic construction system will be applied to two test construction sites by the end of the project to confirm its usefulness and pave the way for practical application.

R&D theme (a-2)
Autonomous measurement and construction technology for inaccessible locations
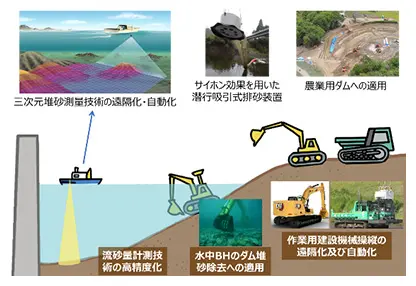
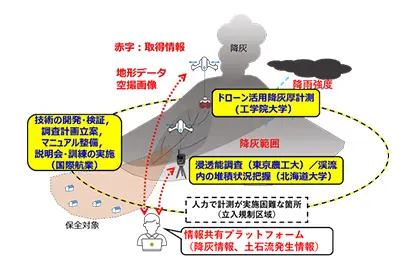
The goal of R&D theme (a-2) is to establish unmanned measurement and construction techniques for real dam reservoirs and volcanic disaster sites, with the aim of reducing the number of worker fatalities and injuries at sites that are difficult to access by humans. Specifically, the following research topics will be addressed
- Remote control and autonomy of construction machines for dam sediment control.
- Remote underwater excavation and dredging for dam sediment control.
- Novel technology for discharging sediment near the dam embankment downstream during flooding.
- Advancement of monitoring technology for sediment management at dams (3D sediment surveying technology, sediment condition monitoring technology, sediment volume measurement technology).
- Practical application of a drone to survey ash fall thickness during volcanic eruptions.
- Ash-fall-data acquisition technology using drones during volcanic eruptions.
- Development and field verification of a technology to detect debris flows during volcanic eruptions.
- Development and field verification of technology to investigate ash fall quality during volcanic eruptions.
The above research will be conducted in parallel with the development of elemental technologies through demonstration tests in real dam reservoirs or volcano sites. These elemental technologies will be integrated into a dam dredging and monitoring system and a volcano observation system by the end of the third year of the project. By the end of the project, integrated demonstration tests (scenario tests) will be conducted in actual dam reservoirs and volcanic environments to confirm the usefulness of the integrated technologies and pave the way for their practical application.
R&D theme (a-3)
Automated Construction for Tunnel Blasting
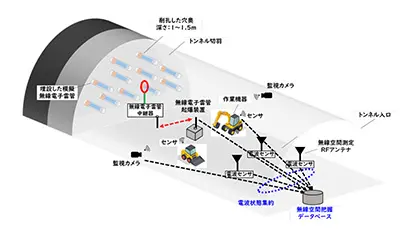
The objectives of R&D theme (a-3) are to achieve practical application of wireless electronic detonator systems and to standardize electronic detonators, with the goal of automating and conducting unmanned operations for the hazardous work of tunnel blasting. Specifically, the following research topics will be addressed
- Development of a wireless communication system for electronic detonators.
- Development of wireless electronic detonators with high safety features.
- Development of wireless electronic detonators for mechanical loading.
- Investigation of evaluation methods for construction safety during tunnel blasting.
The aforementioned elemental technologies will be developed concurrently to achieve a wireless electronic detonator suitable for use at actual tunnel sites by the end of the third year of the project. By the project's conclusion, this detonator will be adapted for integration into the tunnel explosives mechanical loading system under development by various construction companies. Blasting tests will then be conducted in simulated and trial tunnels to validate the effectiveness of the proposed system and facilitate its practical application.
Innovation & Giving Back to Society
In order to accelerate the research and development of remote and automated technologies, this project aims to develop a information sharing interface for automated construction. As a result, it is expected that mutual utilization of technology and entry of new companies for automated construction will become possible, enabling not only major general contractors but also local construction companies to utilize this system.
Furthermore, research and development will be conducted on unmanned automated measurement and construction technology using robots and other devices, as well as on the automation and unmanned operation of hazardous tasks such as tunnel blasting.
As a result, it will be possible to contribute to ensuring the safety of workers and improving productivity in challenging or hazardous construction sites where manual implementation is difficult.

Greeting Greeting
This is Keiji Nagatani, the project leader for "Subproject A: Innovation in Construction Production Processes."
In recent years, expectations for tele-operated/automated construction using robotics and ICT technologies have been on the rise, driven by a shortage of workers and a shrinking workforce in the construction industry. In this project, we will develop tele-operational and/or autonomous technologies, such as "automated earthworks," "surveillance and construction technology for inaccessible areas," and "Automated tunnel blasting."
In such target sites, we are confronted with the challenges of "diversity and uncertainty." Even for the same type of construction or the same type of target object, there are often significant variations in work procedures due to the diversity of the environment. In other words, the level of uncertainty in an outdoor construction site far surpasses that of an indoor manufacturing site, such as a factory. Historically, this challenge has been addressed through the knowledge and experience of on-site operators. However, with automated technologies, there are no skilled operators available to manage uncertainty in site conditions. Therefore, the tasks targeted in this project are inherently very challenging.
Therefore, in this project, we aim to automate construction machinery and related devices, and by incorporating remote operation for tasks that require the experience of skilled workers, we will achieve manpower reduction (and/or unmanned operation) at construction sites. Furthermore, by advancing the social implementation of the developed technology, we will ensure on-site worker safety while enhancing productivity.
Project Leader, Subproject A
Professor, Institute of Systems and Information Engineering, University of Tsukuba
Keiji Nagatani

Members Members
R&D theme (a-1)

R&D Theme (a-1) Leader
Institute of Systems and Information Engineering, University of Tsukuba
Keiji Nagatani
Joint Research and Development Organization
-
- Principal Investigator
-
Kyushu University
Yasuhiro Mitani
- Principal Investigator
-
Kyushu University
Ryo Kurazume
-
- Principal Investigator
-
Public Works Research Institute
Takeshi Hashimoto
- Principal Investigator
-
Fujita Corporation
Takumi Chiba
R&D theme (a-2-1)

R&D Theme (a-2-1) Leader
Public Works Research Institute
Koichi Mizukusa
Joint Research and Development Organization
-
- Principal Investigator
-
Taisei Corporation
Hiroaki Aoki
- Principal Investigator
-
Water Resources Environment Center
Masato Ono
-
- Principal Investigator
-
National Agriculture and
Food Research OrganizationAkie Mukai
- Principal Investigator
-
Kyoto University
Kota Koshiba
-
- Principal Investigator
-
Sea Plus
Keizan Murakami
- Principal Investigator
-
Japan Water Agency
Masafumi Ando
-
- Principal Investigator
-
Shinshu University
Daizo Tsutsumi
R&D theme (a-2-2)

R&D Theme (a-2-2) Leader
Kogakuin University
Yasushi Hada
Joint Research and Development Organization
-
- Principal Investigator
-
Kokusai Kogyo Co.
Toru Shimada
- Principal Investigator
-
Hokkaido University
Takashi Koi
-
- Principal Investigator
-
Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology
Katsushige Shiraki
R&D theme (a-3)

R&D Theme (a-3) Leader
The University of Electro-Communications
Takeo Fujii
Joint Research and Development Organization
-
- Principal Investigator
-
NOF Corporation
Toshiyuki Ogura
- Principal Investigator
-
Japan Construction Machinery and Construction Association
Hidekazu Terato
-
- Principal Investigator
-
Kumagai Corporation
Kenichi Sugimoto
- Principal Investigator
-
Taisei Corporation
Shingo Miyamoto
-
- Principal Investigator
-
Maeda Corporation
Kazuhiko Mizutani









-jpg.webp)




